1.2 Development status2
1.2.1 Operation Model
In line with its structural advantages of geographic proximity and each university or college featuring its own outstanding majors, the CTCCR uses a “one-school” operation model, forming a single virtual school. In teaching, each school selects its superior quality educational courses as optional courses open to all students of CTCCR, and credits are recognized by all member institutions. In teaching management, coordinated planning through the virtual school takes into consideration all possible angles, and resource sharing is realized using unified management and distributed implementation. The “one-school” operation model is achieved in two ways. One is to create a “one-school” teaching management system centered around teachers and students, and the other is to formulate a “one-school” course system oriented to overall development of students.
1.2.2 Teaching management system
Corresponding to the three-level management model of president, dean and academic affairs section in each individual higher education institution, CTCCR uses a three-level management model of board of directors, association of section chiefs and management office. The organizational structure is as shown in Figure 1:

Figure 1 Organizational Structure of CTCCR
The board of directors consists of all member institutions, with Beijing Municipal Commission of Education acting as chairperson. A regular annual meeting is held to make decisions on major issues concerning base development and to instruct the management office to implement such decisions. Other meetings of the member institutions are held as needed to research and settle important problems in a timely manner.
The association of section chiefs is made up of the executive chiefs of the academic affairs sections of all member institutions. Regular meetings are held once every six months to review work done in the past period, report the financial situation, make arrangements for work in the next period, and discuss how to solve specific problems concerning all members.
The management office is made up of the executive chiefs of the academic affairs sections of six vice chair institutions. Currently, the office is located at Beijing University of Aeronautics & Astronautics (Beihang University), and it is mainly responsible for organizing the drafting of management documents and day-to-day administration details. Solutions to major issues are put forward for the chairperson’s and vice chairperson's examination and approval.
Six teams, each responsible for different functions, work under the direction of the management office. Each team is made up of five member schools.
1.2.3 Course system
CTCCR achieves credit transfer through three levels of teaching: cross-institution public optional courses, “cross-institution minors” offered by individual member schools, and “CTCCR minors” jointly offered by multiple member schools. These three levels constitute the course system of CTCCR.
Up to 2009, CTCCR offered over 1,200 course instances with student attendance exceeding 100,000 times. CTCCR cross-institution optional courses reached an average of 40% of total optional courses and 8% of total credits.
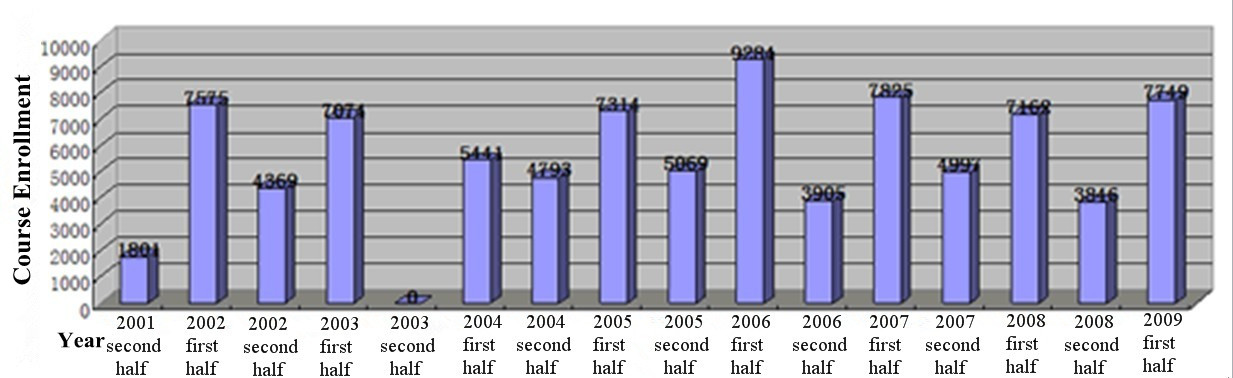
Figure 2 Distribution of CTCCR Cross-institution Course EnrollmentOver Ten Years1
Up to the 2011 autumn semester, the system of cross-institution public optional courses expanded to the point of including 11 disciplines (excluding military affairs) and 265 rationally distributed cross-institution optional courses.
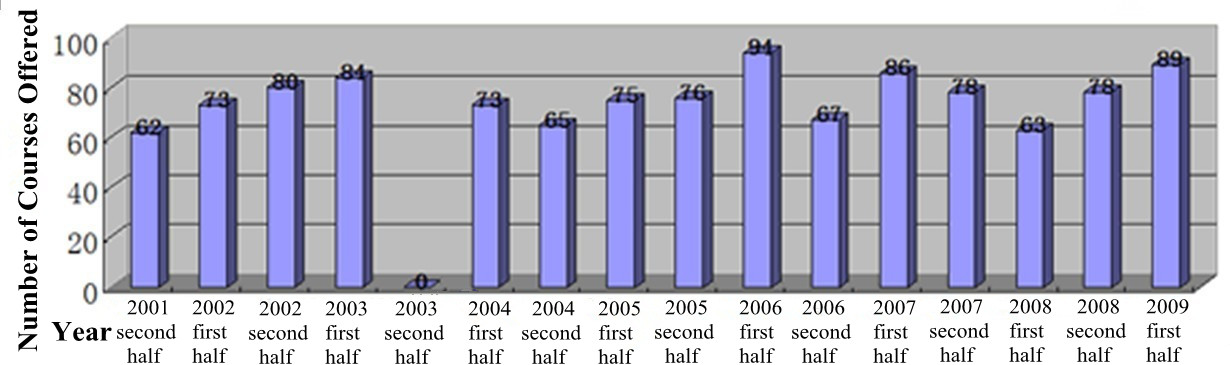
Figure 3 Distribution of CTCCR Cross-Institution Courses Offered Over Ten Years2
CTCCR selected member schools with obvious disciplinary strengths and established 34 “cross-institution minors”. Examples include Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications' “telecommunication engineering” and Beijing Sport University's “human sports science (athletic health care orientation)”, “sports management”, etc.3
Many of the member schools worked together to establish 16 “CTCCR minors”4,and quite a number of them are new disciplines not included in the national list of disciplines, such as “headquarters operation and management”, “exhibition economics and management”, etc.
1.2.4 Quality assurance of credit transfer
To ensure teaching order and quality, CTCCR established a complete quality supervision system with board of director regulations as the root and relevant teaching management regulations issued at the proper time as branches. The system includes unified teaching organization, management and implementation directives for each school to carry out. Major management systems include CTCCR Regulations for Board of Directors, Regulations on Teaching Management of Cross-Institution Public Optional Courses, and CTCCR Rules for Organization, Management and Implementation of Minors, etc.
To guarantee the convenience of students studying within CTCCR, a CTCCR portal site (http://www.xueyuanlu.cn/) was launched in 2001, and a CTCCR interactive platform for teaching, management and services was established to ensure effective “one-school” teaching management from a technical standpoint. All students can select courses, participate in tutorial Q & A, submit assignments, and view and manage scores via the website. Operational management functions continue to be moved online, with some courses offering distance online teaching and distance examinations.
1.3 Implementation results
The implementation of CTCCR provides students with diversified choices. The diversified courses attracted as many as 160,000 student visits. For the member schools, “complementary sharing of educational resources produces a win-win situation for all of the schools. Their limited manpower, material resources and funds are better used in promoting the development of each individual school, opening up a prospect for different campus cultures to integrate and develop side by side.” (XIONG Qingxu, 2012)³ To this end, CTCCR is also listed as a key project for educational system reform by the state and Beijing Municipality, garnering praise and attention from people in all fields.