III.THE DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF THE I-EXPERIMENT ONLINE SUPPORT PLATFORM
The “i-experiment” online platform constructed during the research shapes the “i-experiment” series application websites and matching online resource systems based on the research achievements of the model.
The construction of the “i-experiment” platform is based on the educational resources of the Open University of China (OUC) and its cooperative vocational universities and enterprises for professional development and life skills in line with the principle of “serving the public and encouraging innovation”. This is achieved through a range of online practical education activities, such as i-creation, i-calligraphy, i-singing, i-apparel, i-ecological garden, i-3D printing, and i-digital, thus shaping a harmonious online and offline ecosphere for all participants, including teachers, students and the community. The trial website for the “i-experiment” online support platform is http://www.shequ.edu.cn. Figure 1 shows the technical route, overall framework and functional realization of the platform:
A.Overall system framework
The system will be made up of several modules that are loosely coupled with each other. They can work together or independently for step-by-step implementation within the project.
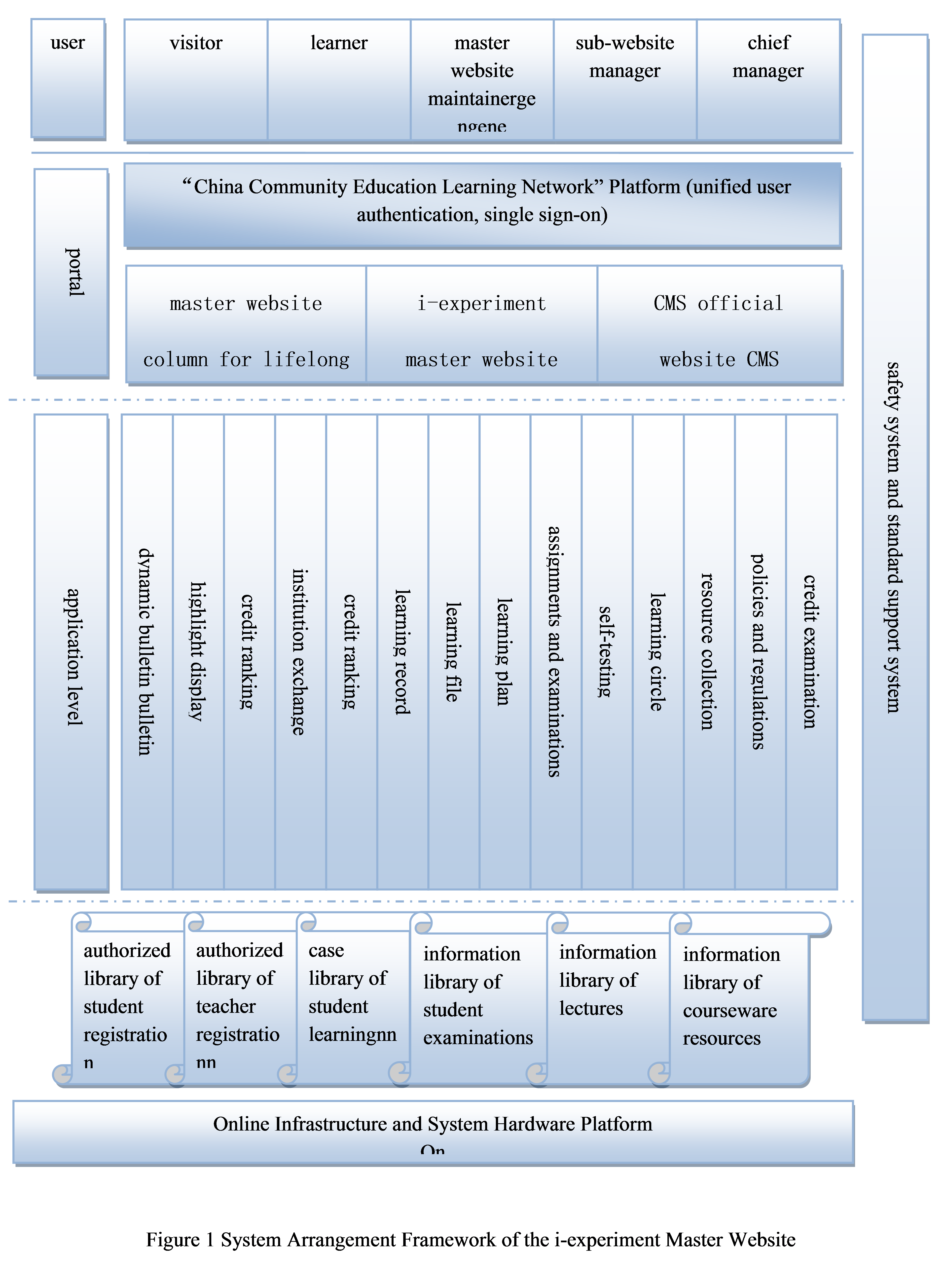
B.Functional structure of the platform
The major functions of the i-experiment master website cover the six aspects of openness, learning, course, action, management and services, as seen in Figure 2.
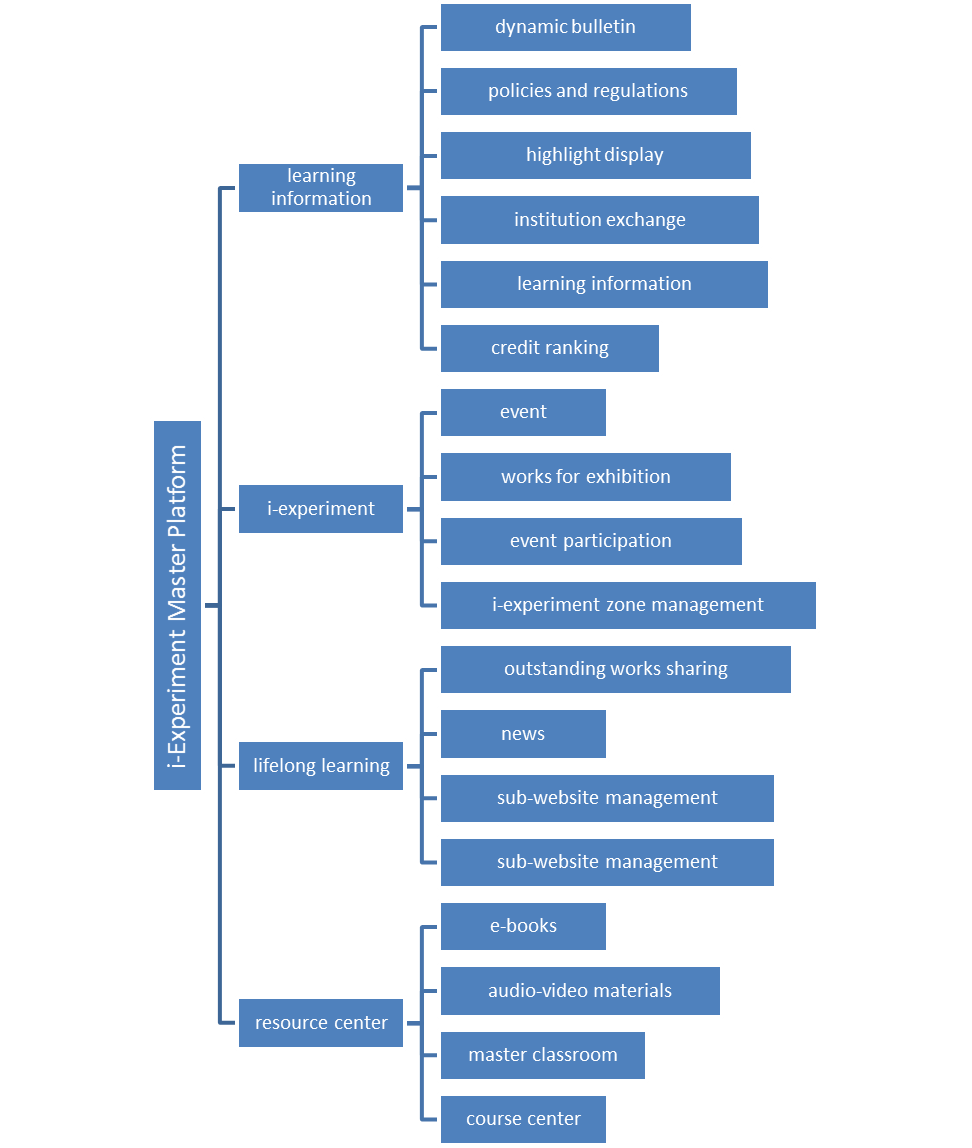
Figure 2 Functional Structure of the i-Experiment Master Platform
“Openness” embodies the complete openness of all kinds of resources. “Learning” expresses learning activities, including plans, notes, tests, and communities. “Course” represents resources, such as famous teachers, books, and audio-visual programmes. “Action” signifies interaction. Both visitors and learners can participate in their favorite projects. “Management” emphasizes the reinforcement of standards to create a strong ecosphere. “Service” focuses on orientation to meet the diverse needs of different learners.
Efforts have been made to try to innovate some of these website functions. The first is the integration of the community education network. The function of integrating local lifelong learning networks and third party resources is to bring together outstanding resources, and to shape them for online learning through the metadata information of various local resources. In the meantime, corresponding learning records are obtained through methods such as data capture. The contents integrated include a special i-experiment network and local courses for lifelong learning. The second is single sign-on. The i-experiment website has a “community education” channel, which integrates and stores resources from local lifelong learning worksites and learning service programmes as well as links to skip ahead. When they visit “community education” courses and service programmes, learners can skip to relevant “local community learning networks” (or one of the theme websites of the i-experiment project). Though they have their own independent user system and verification mechanism, learners can visit all the relevant application systems once they have logged on the master website, obtaining synchronous learning records from the master website and the “local community learning network” (or one of the theme websites of the i-experiment project). The third is resource integration. The objects of resource integration include course resources, dynamic information and other learning resources from the “local community learning network” (or one of the theme websites of the i-experiment project). The core information of these resources is stored in the resource database and provided by the network in accordance with its standards. The integrated resources are released by the master website and pushed to the “local community learning network” (or one of the theme websites of the i-experiment project) via the interface.