III. Basic principles of construction of mobile learning resources
Based on the above analysis of the characteristics of mobile learning, the basic principles of construction of mobile learning resources are:
1. Suitable principle: This contains two parts. The first refers to the presentation of resources fit for mobile learning devices, which take advantage of the characteristics of mobile learning devices including sound, text, graphics, animation, rich media forms and instant interactivity. The second refers to learning resources designed to fit target groups. Full consideration of the learner's age, educational background, learning styles and so on is taken into account. [4]
2. Miniaturization principle: Mobile learning using fragmented time requires that the amount of learning content not be too large to ensure content can be completed. Therefore, mobile learning content should use one point of knowledge of miniaturization to ensure that learners master study materials in a short period of time without interference. [5]
3. Refining principle: Given the limited time available to design the contents of refining, problem-solving is very important. Learning content is closely related to a student’s learning ability, life and work. Providing a single theme has practical significance. It can both stimulate and sustain continuous learners in mobile learning motivation and learning interest. Media presentation adopted in the form of resources should be targeted. There are few images and videos not only because information transmission will impact learning effect, but also because the data flow causes an increase to learning costs. [6]
4. Differences principle: Based on differences in motivation and learning ability, learners are divided into autonomous learning, latent learning, collaborative learning and passive learning categories corresponding to mobile learning resources.[7] The presentation should be open and suitable for students with different learning styles, interests and incentives to encourage participation in interactive modules. This fosters a positive learning attitude in the learning process.
IV. The OUC’s learner analysis
Distance education is a resource-based form of education. The Open University of China’s (OUC) functional role cannot be achieved without the support of learning resources. As a new university, the unique values of the OUC are fully apparent in its learning resources.[8] In recent years, students at the OUC showed the following characteristics.[9]
1. Relative to college students, adult learners generally have their own work and family commitments. They experience the conflicts between work and study, limited learning time and energy. Their concentrated learning time is more likely to be limited. Mobile learning allows them to learn anytime, anywhere, and receive timely feedback on learning, communication and discussion.
2. Learners are progressively of a younger age. Most learners fall into 18 to 25 years of age learning group. This trend means that the majority of learners have less than five years’ work experience.
3. As the post-1980s generation has grown up under the conditions of a market economy, most students of this group own a personal computer or laptop. Online learning is therefore very convenient and accessible given their advanced ICT ability.
4. There are high expectations for flexible, effective teaching and learning methods and effective learning support services. Findings from learning expectations survey show that students’ learning time and learning expectations focus on flexible and effective ways of teaching and learning. Students expect schools to provide comprehensive and efficient learning support services.[10]
The China Internet Network Information Center (CNNIC) released its 32nd Survey Report at the end of June 2013 that showed China's number of the Internet users has hit 591 million, with 464 million cell phone users. The proportion of users accessing the Internet with their cell phones increased to 78.5 percent. Therefore, mobile learning resources development is of great significance.
V. "Operating system" course design-based pad
“Operating System” is a professional course for Computer Science and Technology majors. The course design is in accordance with the offline mobile learning mode-based pad. Digital course materials are stored on the portable device pad allowing students to learn anytime, anywhere. Mobile learning theory is based on informal learning, the unconscious mind and memory law.[11] Resources are in the form of documents, images, audio, video, software and streaming media. Learners can use their time to learn, work and rest. This method of learning fits with the lifestyles of people who are busy yet need to learn. They can learn on the way to work, on a business trip and use fragmented time to learn using interactive learning resources. Evaluation methods can be used for practicing and testing learning content.
1. Design of learning content
The first step of mobile learning resource development is to determine the content for learning, which is based on teaching goals and analysis of mobile learning terminal device characteristics. Different resources, such as online courses and digital textbooks, contain different teaching methods to play to respective strengths and solve teaching problems. Students can learn according to their own needs and ways by selecting appropriate media in order to achieve optimal learning.
Digital textbooks are not only electronic versions of printed materials. Compared with printed materials, digital textbooks increase computer and network capabilities to insert rich media forms, notes management and sharing. Furthermore, their production cost is low and orders can be placed per chapter. Most importantly, digital textbooks are easy to update and suited to students and teachers involved in the development of teaching materials.[12] In comparison with online course, greater emphasis on consistency of internal structure is placed on digital textbooks to avoid the simple collection of all types of resources. One aim of digital textbooks is to accommodate remote learning via tablet PCs and other mobile devices. Currently, digital textbooks are used extensively at the Open University of the UK and other distance education institutions.
1.1 Organized by the theme of learning content
The example provided below shows an operating system and its relation to course content through a top-down module network. The content is sub-divided into various modules and sub-modules. By dividing content of a subject into modules, relatively independent learning content is assigned as appropriate. The operating system’s memory management functions are shown below:
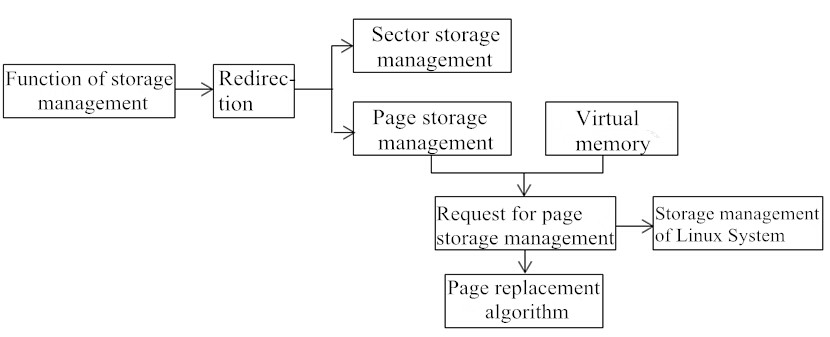
Figure 1: Storage management capabilities and knowledge structures
In order to facilitate understanding of the structure of content, learners browse a knowledge structure diagram before they begin to learn course. This is to figure out the inherent logic of thematic content and guide them in making reasonable arrangements to learn.