Table 4 Proportion of reference points for individual reasons for dropping out during the three semesters observed
|
First observed semester |
Reasons for dropping out |
Proportion of reference points (%) |
Second observed semester |
Reasons for dropping out |
Proportion of reference points (%) |
Third observed semester |
Reasons for dropping out |
Proportion of reference points (%) |
|
Dropouts |
Internal factors |
52.4 |
Dropouts |
Internal factors |
58.0 |
Dropouts |
Internal factors |
41.5 |
|
—Academic integration |
27.9 |
—Academic integration |
31.6 |
—Academic integration |
24.4 |
|||
|
—Social integration |
24.5 |
—Social integration |
26.4 |
—Social integration |
17.1 |
|||
|
Psychological experience |
33.0 |
Psychological experience |
22.1 |
Psychological experience |
45.5 |
|||
|
—Heavy cognitive load |
27.2 |
—Heavy cognitive load |
16.0 |
—Heavy cognitive load |
35.0 |
|||
|
External factors |
14.6 |
External factors |
19.9 |
External factors |
13.0 |
|||
|
—Conflict between work and study |
9.5 |
—Conflict between work and study |
13.9 |
—Conflict between work and study |
4. 9 |
|||
|
Professional tutors |
Internal factors |
37.1 |
Professional tutors |
Internal factors |
36.8 |
Professional tutors |
Internal factors |
35 |
|
—Academic integration |
33.7 |
—Academic integration |
20.6 |
—Academic integration |
30 |
|||
|
—Social integration |
3.4 |
—Social f integration |
16.2 |
—Social integration |
5 |
|||
|
Psychological experience |
50.6 |
Psychological experience |
35.3 |
Psychological experience |
55 |
|||
|
—Heavy cognitive load |
41.8 |
—Heavy cognitive load |
20.9 |
—Heavy cognitive load |
40 |
|||
|
External factors |
12.4 |
External factors |
27.9 |
External factors |
10 |
|||
|
—Conflict between work and study |
4.5 |
—Conflict between work and study |
19.1 |
—Conflict between work and study |
5 |
|||
|
Teachers in charge of daily management |
Internal factors |
26.0 |
Teachers in charge of daily management |
Internal factors |
17.8 |
Teachers in charge of daily management |
Internal factors |
12.5 |
|
—Academic integration |
20.5 |
—Academic integration |
13.7 |
—Academic integration |
12.5 |
|||
|
—Social integration |
5.5 |
—Social integration |
4.1 |
—Social integration |
0 |
|||
|
Psychological experience |
28.8 |
Psychological experience |
20.5 |
Psychological experience |
12.5 |
|||
|
—Heavy cognitive load |
24.7 |
—Heavy cognitive load |
16.4 |
—Heavy cognitive load |
12.5 |
|||
|
External factors |
45.2 |
External factors |
61.6 |
External factors |
75 |
|||
|
—Conflict between work and study |
34.2 |
—Conflict between work and study |
34.2 |
—Conflict between work and study |
56.3 |
Proportion of reference point=individual discontinuation reason reference point/entire discontinuation reason reference point
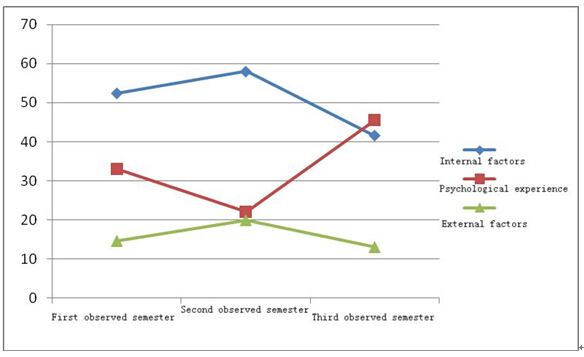
Figure 6 Comparison of reasons for dropping out during the three semesters (dropouts)
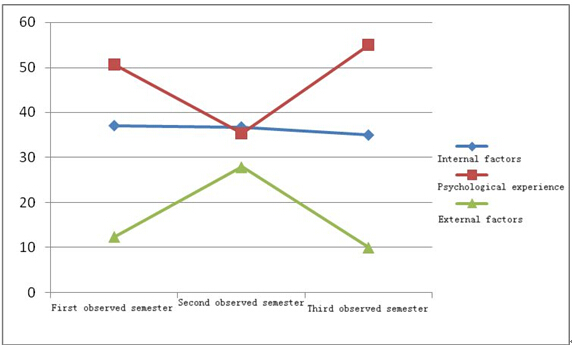
Figure 7 Comparison of reasons for dropping out during the three semesters (professional tutors)
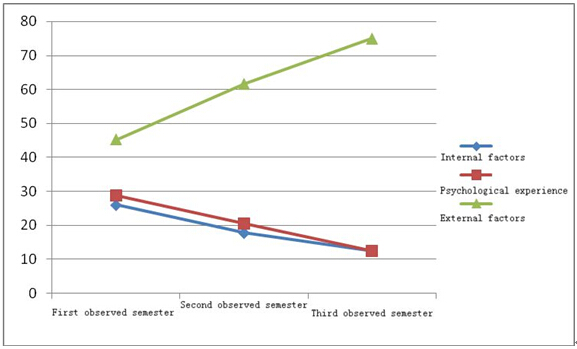
Figure 8 Comparison of reasons for dropping out during the three semesters (teaching assistants)
By analyzing the reasons driving dropout rates from bachelor’s degree programmes, we can identify what leads to a failed ODL experience. We can observe common reasons for dropping out over the course of the three semesters. It points to a lack of time management and ICT-based learning, both of which are essential to ODL. In addition, many ODL students do not have a strong background of English education, which means they must put in more effort. Due to a lack of abilities, they find it hard to adjust to university life, creating a negative psychological experience after enrollment. A lack of motivation to engage in ICT-based learning makes it difficult to fit into the ODL system, which is characterized by a combination of face-to-face tutorial and online tutorial and doesn’t guarantee enough interaction with other students and tutors. A lack of time management leads to weaker learning input due to conflicts between work and study. All these reasons contribute to heavy cognitive load, low confidence in English learning ability, loss of interest and confidence, and eventually dropping out.